As recent headlines have highlighted, the NHS backlog in routine operations and procedures has reached worrying heights during the pandemic. Data from NHS England shows that currently more than 5 million people in England are waiting for hospital treatment, with 3.63 million fewer elective surgeries carried out between April 2020 and May 2021. Meeting this backlog of care is going to be one of the key challenges for Trusts across the country over the coming months.
To achieve this, every element of a Trust’s service needs to be operating as effectively and efficiently as possible. One critical area that is often overlooked is decontamination and sterilisation services. Without effective surgical instrument sterilisation, even basic procedures cannot be carried out.
This insights article looks at some of the problems Trusts face when it comes to providing sterile services and how they can be addressed within integrated care systems (ICS) in a post-COVID world.
The current SSD landscape
There are more than 3,000 NHS hospital theatres across England, carrying out 10 million theatre operations each year, all of which are supported by sterile service departments at an estimated annual running cost of more than £200m.
Typically, sterile services are provided on-site on a Trust-by-Trust basis and are co-located adjacent to Theatres. The size and scope of this service provision is contingent upon both volume and type of a Trust’s elective caseload. The graphic below shows how this £200m spend breaks down by region and ICS, with percentages representing the proportion spent by each ICS within a region.
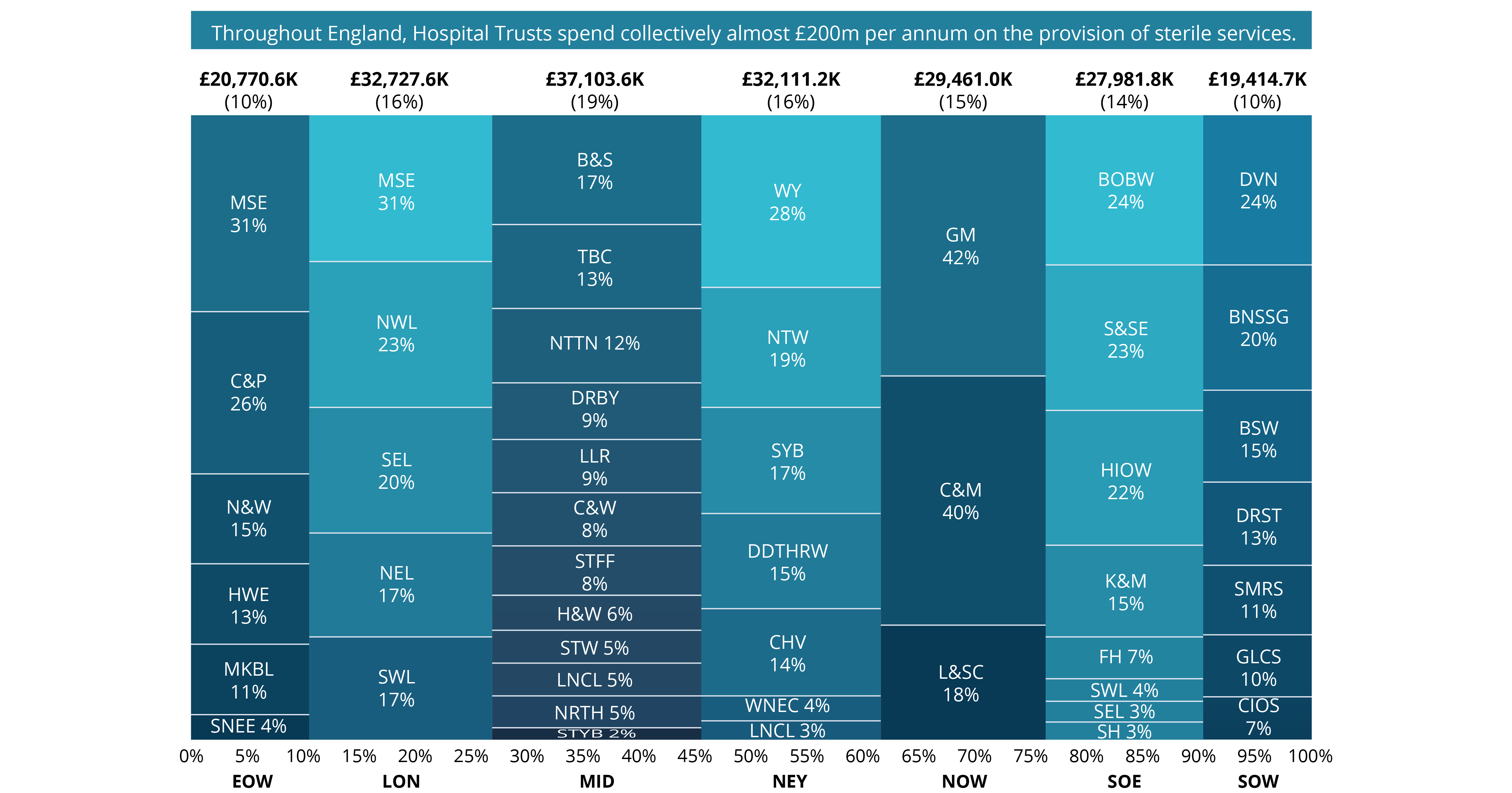
Disparities across NHS Trusts’ Sterile Services
Given the scale of these services, some variation in service performance and delivery is expected. However, digging deeper into NHS Digital data, Akeso & Co found significant disparities across Trusts that need to be addressed.
In fact, the total annual spend on sterile services per ICS, varies extensively in relation to the number of theatres in a Trust and the floorspace their sterile service department takes up. These variations are outlined in the graphic below which plots ICS spending driven by surgical activity and case type, against number of theatres and SSD floorspace.
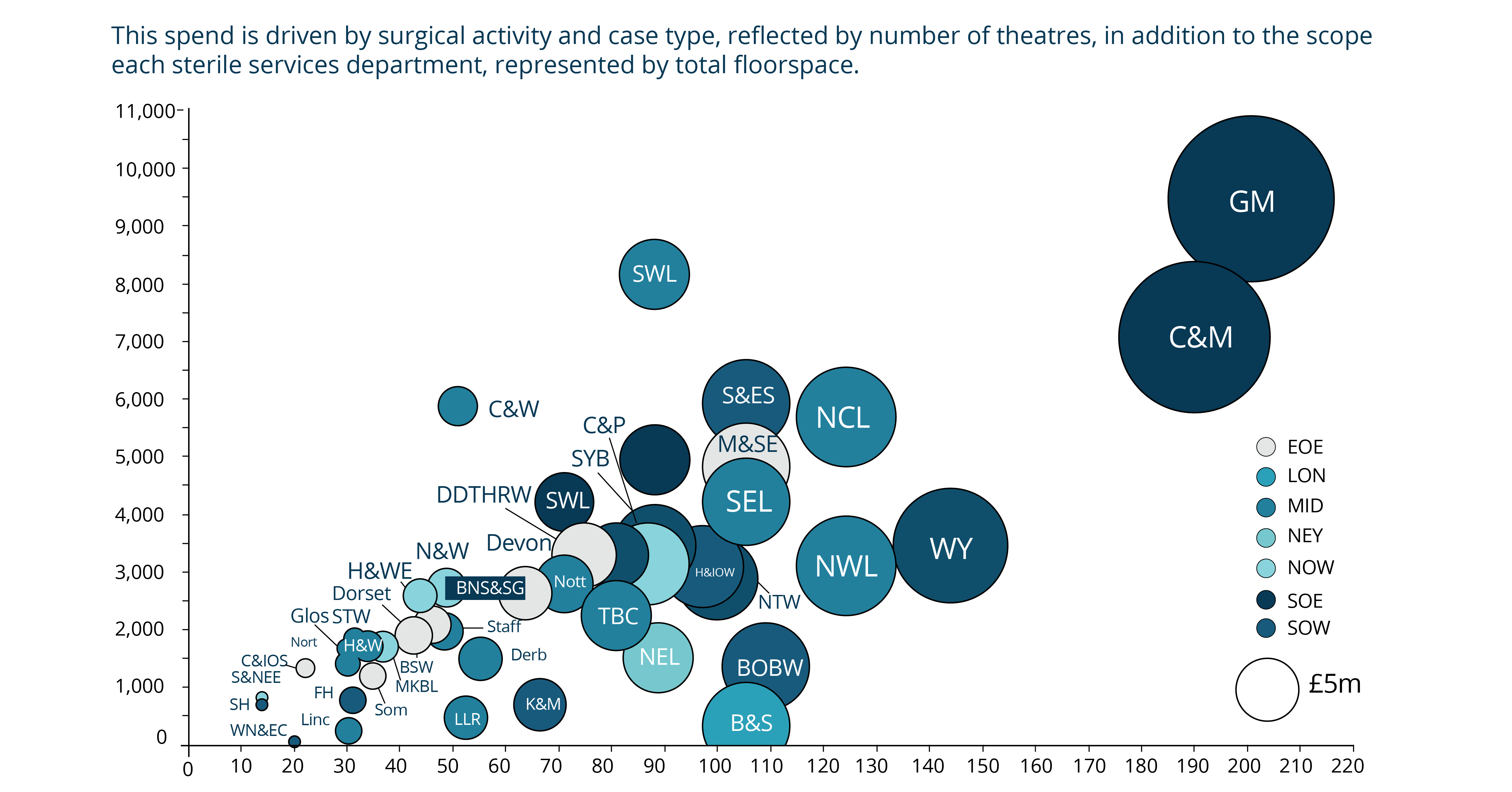
There is significant variation in spend on sterile services by ICS and Trusts when accounting for a hospital’s number of theatres, volume and scope of surgical activity, and unit size. One major cause of this unwarranted variation, highlighted above, is the varying age and condition of sterilisation equipment and assets.
Because the service is capital intensive, with high-value complex assets and costly support facilities, this commonly results in the assets operating beyond their lifespan. Inevitably, this leads to high levels of breakdown, maintenance costs and downtime which impacts a theatre’s ability to operate. In a capital-limited environment, most Trusts do not have the funds to upgrade their sterilisation assets to a standard which would be optimal and compliant.
However, where there is variation in service performance and efficiency, and an increasing backlog of demand, there are clear opportunities for Trusts to improve how they run these services. Trusts should welcome the challenge of further ICS integration as a means of combatting these issues. This will also enable them to redefine operational processes within the entire peri-operative value chain, embrace novel technologies and explore a variety of commercial models.
Addressing the challenges
How Trusts transform sterilisation services to reduce inefficiencies and unwarranted variation will depend on a number of determining factors specific to each Trust. Addressing each one will enable Trusts to create efficient sterile services that allow theatres to function as effectively as possible, as they tackle the backlog of cases caused by Covid-19. Moreover, in reshaping the provision of sterile services, Trusts also have the opportunity to better manage their equipment and explore how they can optimise their floorspace, not least in the context of required theatre expansion programmes, where floorspace is at a premium.
We have identified several factors that will influence a Trust’s decisions, including:
- Hospital site type, number of sites and location
- Level of collaboration within an ICS / STP
- Theatre case volume and type
- State of assets and equipment
- Financial position and capital availability
These all need to be taken into account when considering how to best prepare a Trust for the demands of a post-pandemic world.
To achieve this there are three steps we would recommend taking:
1.Understand the Trust’s requirements and activity
Theatre case volume, case type and surgical preference all impact decontamination activity. For example, orthopaedic surgeries require the greatest volume of associated surgical equipment and, in turn, sterilisation. Moreover, in larger Trusts, having a detailed understanding of the relationship between multi-site and multi-organisation environments is crucial. Only once the demand on sterile services has been accurately understood, can Trusts begin planning their bespoke sterilisation improvement strategies.
2. Tackle mismatches between theatre activity and decontamination volume
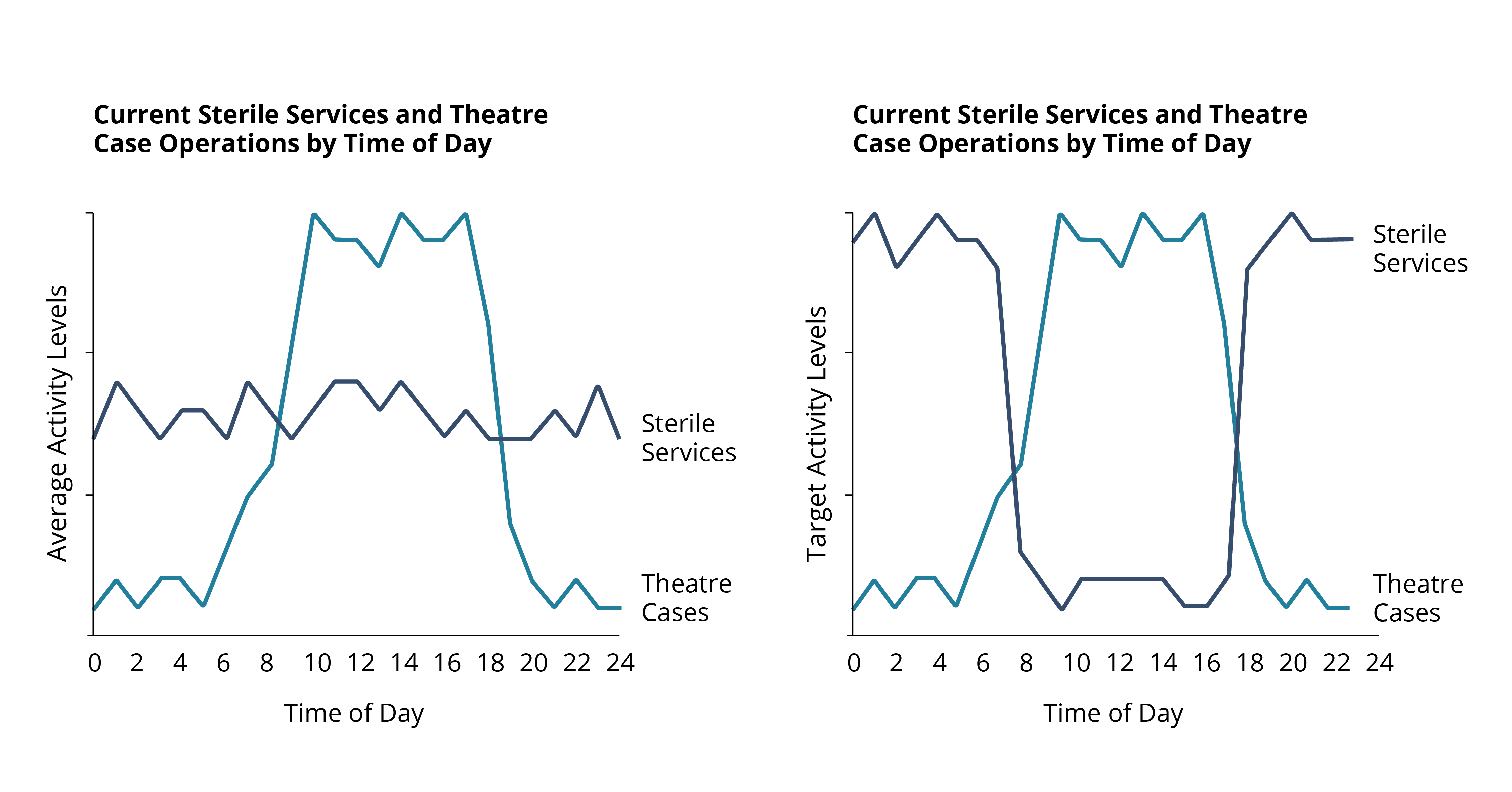
Through improved operational planning, Trusts will be able to manage surgical instrumentation to better meet peak demand and rapid turnarounds when necessary. Currently, the level of sterilisation activity does not always align with the volume of theatre cases, as illustrated in Figure 3 below.
Typically, cases and elective surgeries run throughout the working day, with sterile services running alongside them, often at max capacity. Trusts should look to adopt, where possible, a hybrid working model, whereby sterile service activity is better managed to align with demand and activity. This hybrid model would see the core volume of activity processed outside of the traditional elective window (also shown in Figure 3). This will improve their ability to respond to ad-hoc surgical demand and reduce pressure on already burdened capital assets, enabling crucial machine downtime.
3. Adopt technological capabilities to maximise current operations
Alongside better planning, advances in technology can help ensure the instrument peri-operative value chain is as efficient and effective as possible. Track and trace technologies, such as Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), offer full visibility over surgical instrumentation from surgical use to decontamination and other movements. This enables workflow optimisation and full utilisation of the existing asset base. Work conducted by Akeso & Co discovered that a third of one leading Trust’s surgical instrumentation had not been used for three years, with instrument dormancy going as far back as 2004.
In situations like this, RFID can pinpoint where medical instruments are dormant. Although there are valid clinical reasons for not using certain instruments, a clearer oversight of assets gives Trusts the option to generate value by disposing of unnecessary equipment and freeing up hospital floorspace.
4. Explore a variety of commercial models
There are a number of different commercial models which Trusts should consider, such as joint ventures and managed services that can reduce the significant capital investments required. The graph below shows the range of commercial models currently available, and the different value propositions they offer depending on a Trust’s objectives.
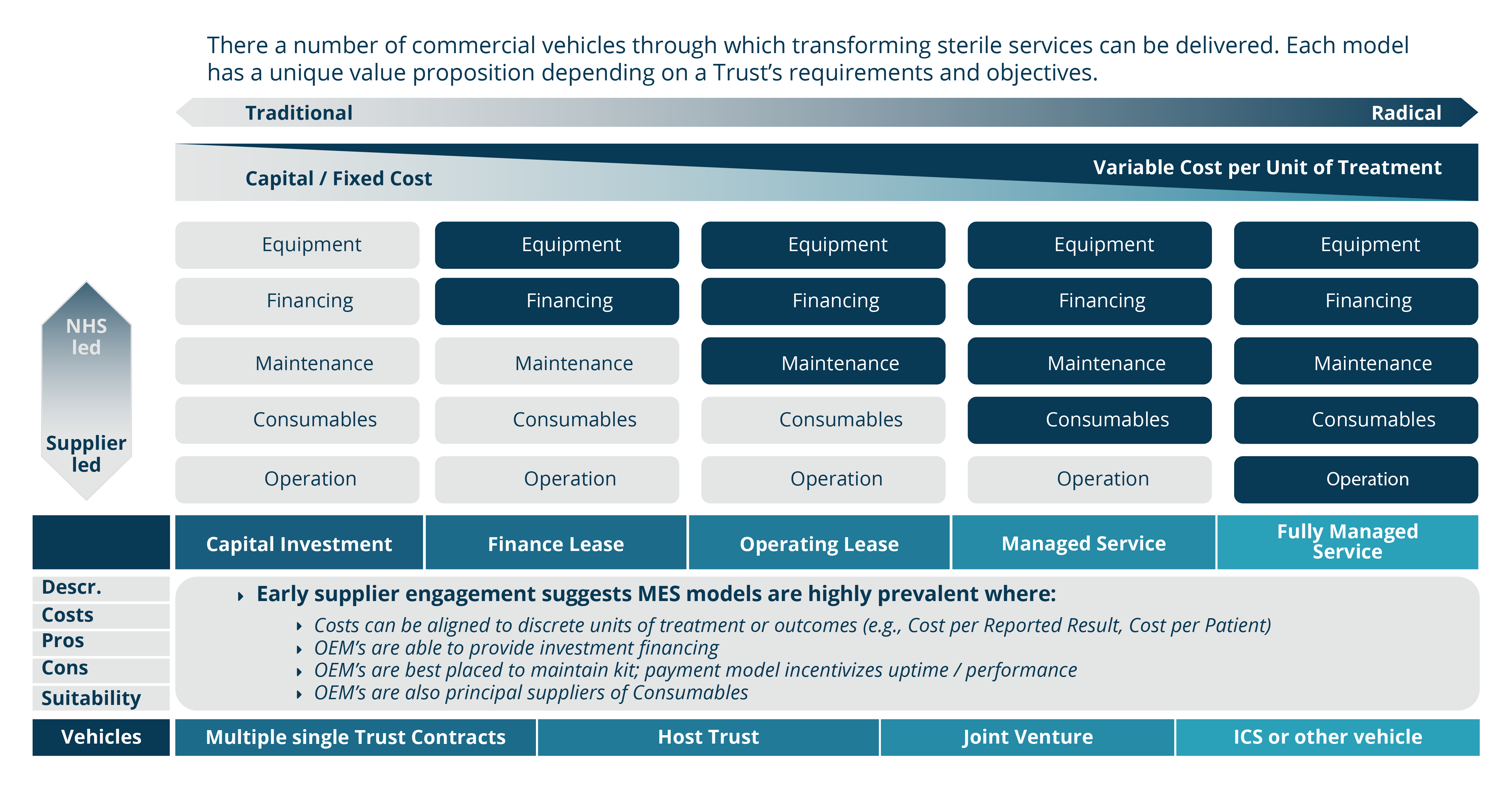
Each commercial model comes with various advantages and opportunities. Depending on the selected model, Trusts have the possibility of further integration within the ICS to share capital and the option of taking sterilisation services off site if appropriate. Further to this, there is the opportunity to create revenue by acting as a lead partner in a commercial SSD network and offering services to the private sector.
Choosing the right model
There are benefits and risks to every solution and weighing up a Trust’s specific needs is an important part of the process when deciding which is the right route to take. We have worked with several Trusts over the years to identify the best direction for their SSD and build a business case to support this.
In transforming sterile services departments, Trusts will put themselves in a stronger position to deal with the fallout from the pandemic. Additionally, this will also increase theatre efficiency, improve infection control measures, generate space savings that enable theatre expansion programmes and potentially create much-needed income.
To discuss how Akeso & Co can help sterile service departments perform their critical role more effectively, get in touch.